101 of 3PL: Scaling Your Supply Chain Without the Headache
08-Jan-2026 - SCM4ALL Team
In the world of commerce, moving a product from point A to point B sounds simple—until you have to manage warehouses, shipping carriers, customs, and returns. This is where Third-Party Logistics (3PL) comes in.
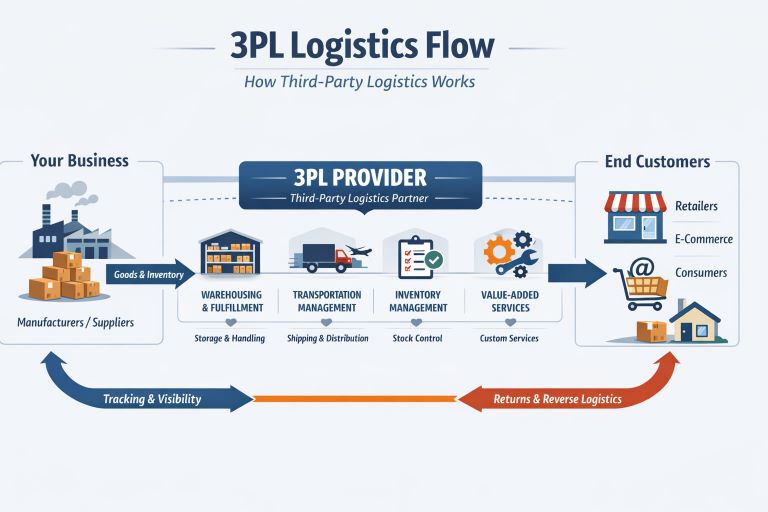
What exactly is 3PL?
A 3PL is a provider that handles outsourced logistics services. Think of them as your "logistics department for hire." They typically manage everything from warehousing and inventory management to picking, packing, and shipping.
Why would someone use a 3PL?
Businesses move to 3PLs primarily to scale without the overhead. Instead of signing a long-term lease on a warehouse and hiring a permanent team, a company can pay for only the space and labor they use. It allows business owners to stop "working in the business" (packing boxes) and start "working on the business" (marketing and product development).
The Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Scalability: Easily handle seasonal spikes without hiring more staff. | Less Control: You aren't the one personally packing every box. |
| Cost Savings: Benefit from their bulk shipping discounts. | Upfront Integration: Syncing your tech with theirs takes time. |
| Expertise: They know international shipping laws so you don't have to. | Cost for Low Volume: Not lucrative if order volume is very low. |
| Advanced Tech: Access to high-end tracking and AI-driven forecasting without the massive upfront investment.. | Hidden Costs:Beware of fuel surcharges, kitting fees, or long-term storage penalties. |
Industry Applicability: Is 3PL Right for You?
- Automotive: Extremely high applicability. These industries rely on Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing where 3PLs manage complex supply chains to deliver parts exactly when needed.
- Food Products: High applicability with specialized partners. 3PLs in this space provide "cold-chain" logistics (refrigerated storage) and ensure compliance with strict food safety regulations.
- Consumer Electronics: High applicability. These high-value, fragile items require secure environments and sophisticated tracking for warranties and serial numbers.
- Household Goods: Moderate to High. Bulky items like furniture benefit from specialized 3PLs that offer "white-glove" delivery and assembly services.
Prominent 3PL Players
- DHL Supply Chain: A global giant known for its massive infrastructure and heavy investment in warehouse robotics.
- ShipBob: A tech-first favorite for e-commerce brands, allowing businesses to spread inventory across multiple warehouses to reduce shipping times.
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions: Ideal for businesses already integrated into the UPS ecosystem, offering seamless global freight and customs brokerage.
Success Stories and Strategic Failures
Successes: Approximately 90% of Fortune 500 companies, including Nike and Apple, publicly leverage 3PL services to manage regional distribution, allowing them to focus on design and marketing.
Failures: A notable cautionary tale is Toys "R" Us in the early 2000s. They outsourced their entire e-commerce and logistics to Amazon. While it worked initially, they eventually lost control over their customer data and brand experience, and Amazon began hosting competing toy brands on the same platform.
The Future: Technology and Onboarding
Will technological advances make 3PLs less lucrative? On the contrary, technology is making them more essential. Modern APIs are making it "plug-and-play" to connect online stores to warehouses. Furthermore, 3PLs are using AI-driven forecasting and autonomous robotics to stay relevant, offering productivity levels that an in-house operation simply cannot match.
By 2026, expect AI for predictive analytics, robotics in warehouses, and strategic roles in network design—growing to $290B+ in the US. Sustainability tracking and resilience post-disruptions will dominate, with 3PLs as agile partners for complex chains.
