📦 Reverse Logistics : Turning Returns into Strategic Value
4-Sep-2025 - SCM4ALL Team
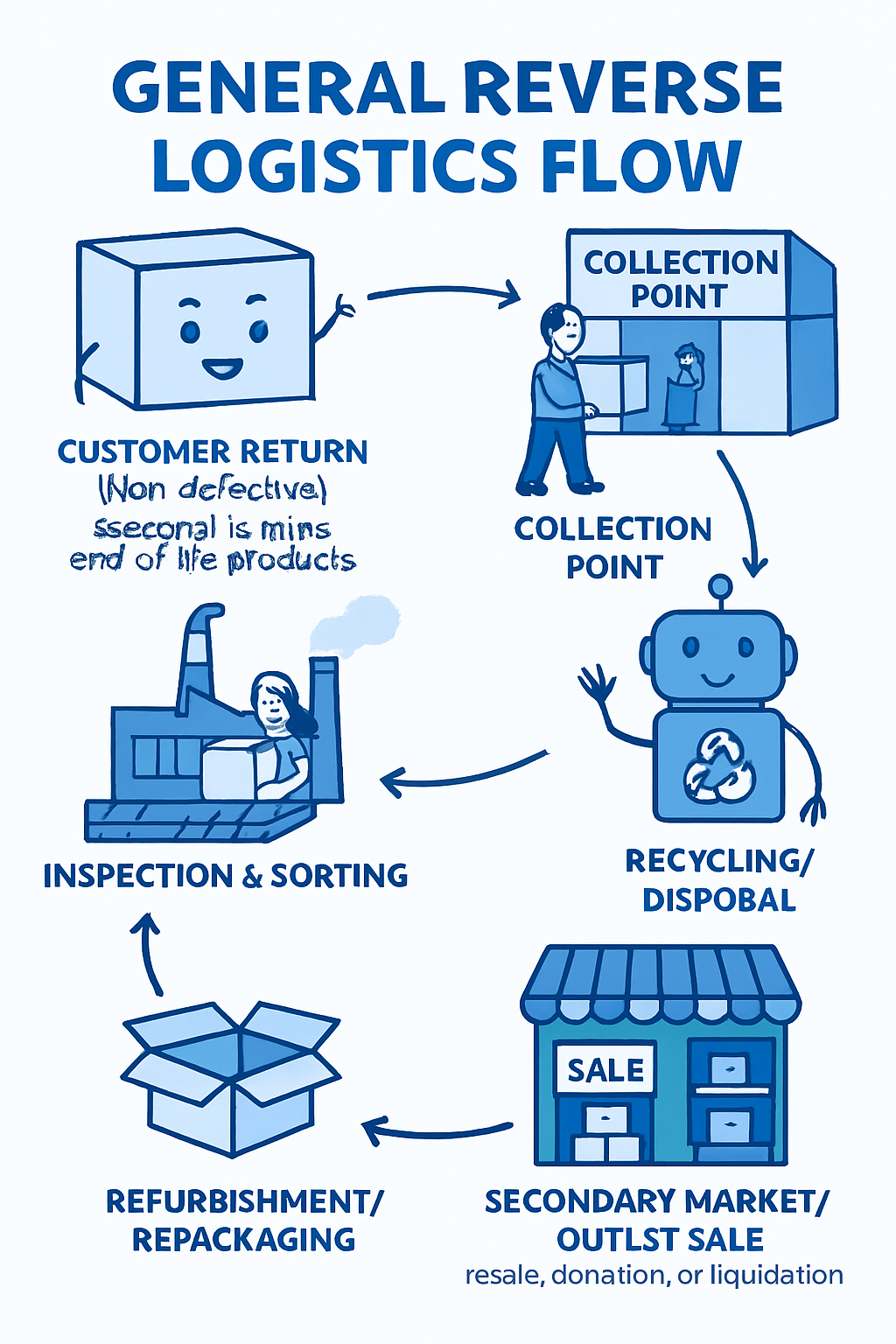
In today’s supply chain landscape, the journey of a product doesn’t have to end at the point of sale. Increasingly, forward-thinking companies are embracing reverse logistics—the process of moving goods from customers back to the manufacturer—for reconditioning and remanufacturing. But how do you convince customers or distributors to send used products back?
Enter: Trade-in credits—a powerful incentive that turns waste into value.
🔄 What Is Remanufacturing, and Why Does It Matter?
Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through cleaning, repair, and replacement of worn parts. Unlike recycling, which breaks products down into raw materials, remanufacturing preserves much of the original value.
Benefits include:
- ✅ Lower production costs (up to 60% savings)
- ✅ Reduced environmental impact
- ✅ Shorter lead times compared to new builds
- ✅ Enhanced brand loyalty through sustainability
💡 Why Incentivize Returns?
Customers rarely return used products without a nudge. That’s where incentives come in—especially trade-in credits, which offer tangible value in exchange for used goods.
Common incentive models:
- 💰 Trade-in credits: Customers receive store credit or discounts on future purchases.
- 📦 Free reverse shipping: Removes friction from the return process.
- 🎁 Loyalty rewards: Points or perks for participating in sustainability programs.
These incentives not only encourage returns but also build long-term engagement and trust.
🏭 Industries Where This Works Best
Remanufacturing is most viable in industries with high-value, durable goods. Examples include:
- Automotive & Heavy Machinery
- Consumer Electronics
- Medical Devices
- Aerospace
- Industrial Equipment Example: Siemens’ Return & Reuse of Automation Components Siemens collects used PLCs, drives, and sensors from industrial clients. These are reconditioned and reintroduced into service or used for spare parts in legacy systems, especially in energy and manufacturing sectors.
Example: Caterpillar’s Remanufacturing Program Caterpillar collects used components like diesel engines, hydraulic systems, and transmissions from customers and dealers. These are remanufactured to OEM specs and resold at lower cost, reducing raw material usage and supporting sustainability.
🔁 Purpose: Value recovery, lifecycle extension, and environmental compliance
Example: Dell’s Take-Back & Refurbishment Program Dell runs a global reverse logistics system to collect end-of-life laptops, desktops, and accessories. Devices are refurbished or recycled, with usable parts reintegrated into new products or sold as certified refurbished units.
🔁 Purpose: E-waste reduction, material recovery, and circular economy support.
Example: Quest International’s Refurbishment Services Medical OEMs partner with Quest to retrieve used diagnostic and surgical equipment. Devices are inspected, repaired, and refurbished under strict ISO and FDA guidelines before being redeployed or resold.
🔁 Purpose: Compliance, cost control, and minimizing downtime in healthcare.
Example: Sterling AOG’s Component Lifecycle Management Sterling supports airlines and MROs by retrieving aircraft parts (e.g., avionics, landing gear) for repair, retrofit, or end-of-life asset recovery. These parts are tracked, refurbished, and returned to service or responsibly disposed.
🔁 Purpose: Asset optimization, regulatory compliance, and uptime assurance.
🔁 Purpose: Sustainability, legacy support, and cost-effective maintenance.
🎯 Designing a Trade-In Strategy: How the industry usually operates
While each individual organisation may have their own strategy, below outlines a broad approach taken by many industries
- Identify Eligible Products – Focus on items with high residual value and remanufacturing potential. Many a times companies need to bake this into their product design strategies at inception stage
- Set Clear Return Criteria – Define acceptable conditions, age limits, and packaging requirements.
- Offer Attractive Trade-In Credits – Make the credit meaningful—e.g., 10–30% off a new purchase or fixed-value store credit.
- Streamline Reverse Logistics – Provide prepaid shipping labels or drop-off points to simplify returns.
- Communicate the Value – Use marketing to highlight environmental impact, cost savings, and product reliability.
- Track and Optimize – Monitor return rates, remanufacturing yield, and customer satisfaction to refine the program.
🌍 The Bigger Picture: Circular Supply Chains
Trade-in programs are more than just clever marketing—they’re a cornerstone of circular supply chains, where products flow in loops rather than straight lines. This model reduces waste, conserves resources, and builds resilience in volatile markets.
For those curious about supply chain management, understanding these strategies is essential. Whether you're designing a reverse logistics flow or evaluating incentive models, trade-in credits offer a compelling blend of economics and sustainability.
Incentivizing in B2C and B2B returns :
As expected, B2B and B2C companies follow similar approaches for incentivising their respective customers to buy into their Refurb/Reman Programs
Lets take a look at how Apple and Caterpillar, giants of consumer electronics and industrial equipments, handle their incentivising strategy
Caterpillar’s Cat Reman® & Certified Rebuild: Industrial Circularity
Core Exchange System
- Customers return used components (called “cores”) to authorized dealers.
- If the core meets acceptance criteria (complete, undamaged), they receive core credit—a discount on remanufactured replacements.
Remanufacturing Process
- Returned cores are disassembled, cleaned, and inspected.
- Advanced salvage techniques like laser cladding, PTA welding, and ultrasonic cleaning restore parts to OEM specs.
- Reassembled components are tested rigorously and backed by a same-as-new warranty.
Product Offerings
- From individual parts (e.g., fuel injectors) to full assemblies (e.g., engines, transmissions).
- Cat Certified Rebuilds include 7,000+ part replacements and 350+ inspections for a like-new machine.
Business Impact
- Lower overhaul costs and downtime.
- Higher resale value and extended asset life.
- Sustainability win: 127 million pounds of material reclaimed in 2021 alone.
Strategic Insight
Caterpillar’s model thrives on dealer relationships, predictable asset lifecycles, and high-value equipment. It’s a B2B ecosystem where uptime, cost control, and long-term ROI matter more than novelty.
Apple: B2C Circularity at Scale
Trade-In Flow
- Customers get an instant estimate online or in-store.
- Devices are returned via courier or dropped off at Apple Stores.
- If eligible, customers receive store credit or discounts on new purchases.
Refurbishment & Recycling
- Working devices are refurbished and sold as certified pre-owned.
- Non-functional devices are disassembled by Daisy, Apple’s recycling robot, which recovers rare earth metals, aluminum, and copper.
- Recycled materials are used in new devices—e.g., MacBooks made from 100% recycled aluminum.
Strategic Goals
- Reduce e-waste and carbon footprint (Apple aims for net-zero by 2030).
- Expand into price-sensitive markets with refurbished products.
- Retain users in the Apple ecosystem, boosting service subscriptions (Music, iCloud, etc.).
Strategic Insight
Apple’s model is built on brand equity, ecosystem lock-in, and consumer convenience. It’s a B2C play where emotional loyalty, ease of upgrade, and sustainability messaging drive adoption.
📊 B2C vs B2B , Apple and Caterpillar: Reverse Logistics Comparison
| Feature | Apple (B2C) | Caterpillar (B2B) |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Consumers, small businesses | Dealers, industrial clients |
| Return Incentive | Trade-in credit, discounts | Core credit, deposit refund |
| Reman Strategy | Refurbishment + material recovery | Component-level + full rebuilds |
| Logistics Complexity | Low – streamlined UX | High – grading, entitlement tracking |
| Sustainability Messaging | E-waste reduction, recycled materials | Lifecycle cost, uptime, ESG |
✍️ Final Thought
As we continue to delve deeper into the SCM world, topics like remanufacturing and trade-in incentives deserve center stage. They’re not just operational tactics—they’re strategic levers for building smarter, greener, and more customer-centric supply chains.
